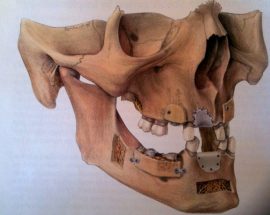
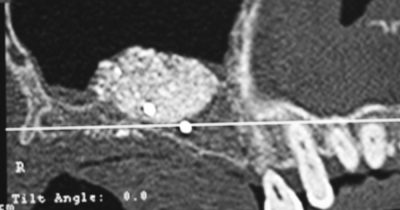
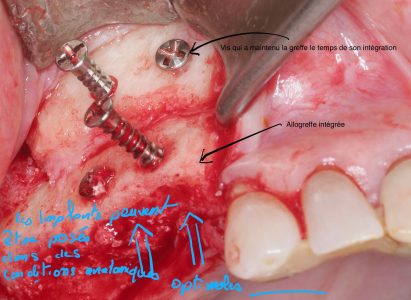
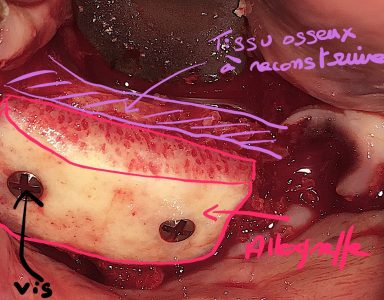
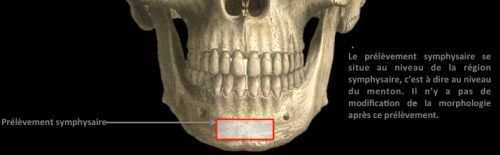
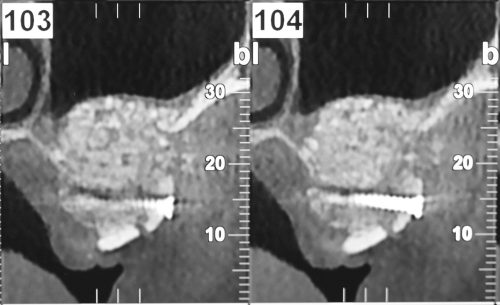
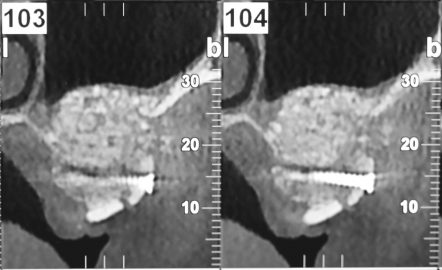
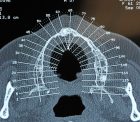
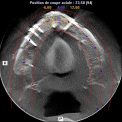
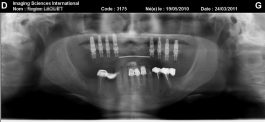
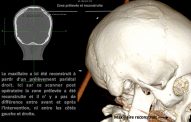
The pre-implant surgery
Your dental surgeon is a medical practitioner who is the best person to give you advice on pre implant surgery and in most of the clinical situations is able to perform the surgery at the dental office.
However, in some cases he may refer you to a maxillo-facial surgeon.
It would be interesting to seek advice from other physicians if a surgery is needed.
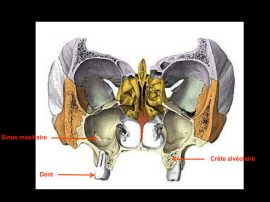
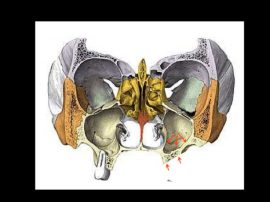
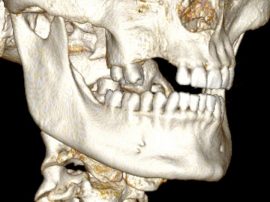
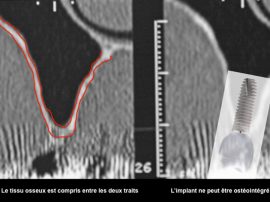
The main purpose of showing these pictures is to provide you with a better comprehension of our techniques.
Each picture outlines aspects of a unique and different clinical situation and could not possibly be transposed.
Prior to placement of dental implant, your dental surgeon will perform a surgical operation for maxillary or mandibular bone reconstruction.